Experiencing blood in your stool after drinking can be a concerning and alarming experience. This potentially serious sign could indicate an underlying medical issue related to alcohol consumption, gastrointestinal health, or other complications.
In this blog post, we will explore the common causes and risk factors associated with bloody stools after drinking, as well as how alcohol affects the digestive system. We’ll also discuss prevention strategies and treatment options to help you maintain optimal gut health while mitigating risks associated with alcohol use.
You Are Watching: Blood In Stool After Drinking Updated 12/2025
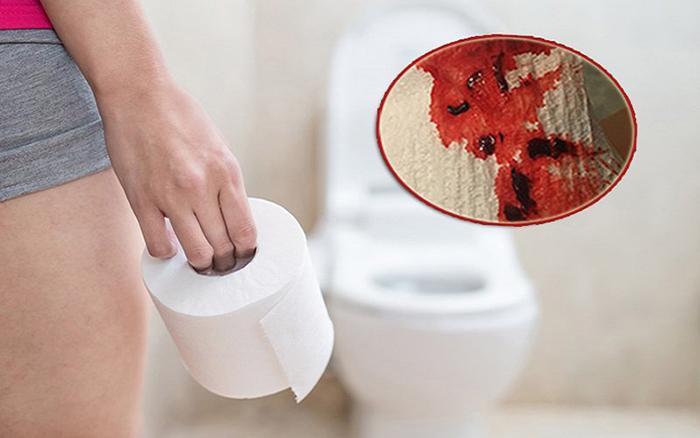
Understanding Blood In Stool After Drinking
Blood in stool after drinking is a concerning symptom that can indicate various medical conditions, including gastrointestinal bleeding, alcohol-induced liver disease, or bowel inflammation.
Common Causes And Risk Factors
There are several common causes and risk factors associated with the presence of blood in stool after alcohol consumption. One primary cause is gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding, which refers to any form of bleeding that occurs within the digestive tract.
Alcohol can irritate the GI tract’s lining, leading to inflammation and ulcers that may bleed.
Another significant risk factor is alcohol-related liver disease (ARLD). It has been well documented that excessive alcohol consumption leads to liver damage, which negatively impacts bowel movements and increases the likelihood of passing blood in stools.
Finally, alcohol is known for increasing an individual’s vulnerability to certain types of cancer – including colon cancer. Approximately one in 17 bowel cancer cases in the UK are attributable to alcohol consumption; hence it serves as a considerable risk factor for developing this life-threatening illness.
In summary, understanding these common causes and risk factors related to finding blood in your stool after consuming alcoholic beverages allows you not only acknowledge their potential dangers but also encourages proactive steps towards prevention and maintaining overall digestive health.
Symptoms And When To Seek Medical Attention
Identifying the symptoms of blood in stool after drinking is crucial for seeking timely medical attention and preventing potential complications. Common indicators of gastrointestinal bleeding include hematochezia, which refers to passing bright red blood along with stool, and melena – black or tarry stools signifying bleeding in the stomach.
It’s essential not to overlook these warning signs or dismiss them as a temporary consequence of excessive alcohol consumption. Persistent symptoms can point toward severe underlying issues like gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), diverticulitis, peptic ulcers, liver damage, or even colon cancer.
Consequently, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional promptly if you experience these concerning patterns following alcohol intake.
How Alcohol Affects The Digestive System

Read More : How Long After Taking Cyclobenzaprine Can I Drink Alcohol Updated 12/2025
Alcohol can irritate the GI tract, increase the risk of GI bleeding, and damage the liver, potentially leading to abnormal bowel movements; read more to learn how to prevent and manage blood in stool after drinking.
Irritation Of The GI Tract
The irritation of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract is a common consequence of excessive alcohol consumption. As alcohol enters the digestive system, it can inflame and irritate the cells in the stomach lining, causing inflammation and ulcers.
A prime example is acute erosive gastropathy, which results from consistent exposure to large amounts of alcohol. This condition often leads to ulcers, erosions, and blood in the stool.
Additionally, duodenitis – an inflammation of the first part of the small bowel – can arise as another outcome from GI tract irritation due to alcohol use.
Increased Risk Of GI Bleeding
Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to an increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, which is a severe and sometimes life-threatening condition.
This type of bleeding typically occurs within the upper digestive tract and can be caused by the irritation of the stomach lining from long-term alcohol use.
Regular alcohol intake can weaken the blood vessels in this area, making them more susceptible to ruptures or tears. Symptoms for GI bleeds include vomiting blood or black stools, indicating that medical attention is required immediately.
Liver Damage And Its Effect On Bowel Movements
Excess alcohol consumption can have a significant impact on liver health, leading to liver diseases such as alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis of the liver.
These conditions can result in severe symptoms, including blood in stool after drinking. Liver damage from heavy alcohol use impacts bowel movements by causing inflammation and irritation of the GI tract.
It’s essential to limit alcohol consumption if you’re experiencing issues with your bowel movements or other related symptoms. Excessive drinking affects various organs, including the liver, pancreas, heart, brain, and immune system.
Maintaining a healthy diet and hydration levels also play critical roles in preventing complications associated with excessive drinking.
Keywords: Alcohol consumption and health; Liver health; How Alcohol Affects the Digestive System ; Alcoholic hepatitis; Cirrhosis of the liver
Prevention And Management Of Blood In Stool After Drinking

To prevent and manage blood in stool after drinking, it is important to limit alcohol consumption, maintain a healthy diet and hydration, and seek medical attention when necessary.
Limiting Alcohol Consumption
Read More : Mexican Yogurt Brands Updated 12/2025
Limiting alcohol consumption is one of the best ways to prevent and manage blood in stool after drinking. Here are some tips for responsible alcohol consumption:
- Set limits – decide how many drinks you want to have before going out.
- Avoid binge drinking – spacing your drinks out over a few hours can reduce the risk of gastrointestinal irritation and bleeding.
- Eat before drinking – consuming food before drinking can help slow down the absorption of alcohol, reducing its negative effects on digestion.
- Drink water – staying hydrated can help prevent dehydration and constipation, which can contribute to gastrointestinal discomfort and bleeding.
- Know your triggers – if certain types of alcohol or situations trigger your symptoms, avoid them.
- Seek support – if you struggle with limiting your alcohol intake, seek support from family members, friends, or a healthcare professional who specialized in addiction treatment.
By following these tips and limiting your alcohol consumption, you can reduce your risk of developing blood in stool after drinking and other associated complications such as liver damage and cancer.
Maintaining A Healthy Diet And Hydration
To prevent and manage blood in stool after drinking, it’s important to maintain a healthy diet with plenty of fiber and stay hydrated by drinking enough fluids. Here are some tips to help you:
- Eat a high-fiber diet: Eating foods that are rich in fiber can help improve your gastrointestinal health and prevent constipation. Some examples of high-fiber foods include whole grains, fruits, vegetables, beans, and nuts.
- Stay hydrated: Drinking enough fluids is essential for preventing dehydration, which can cause diarrhea and increase the risk of blood in stool after drinking. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water per day, and avoid alcohol or sugary drinks that can dehydrate you.
- Focus on electrolyte balance: When you drink alcohol, your body loses electrolytes like sodium and potassium through urine. Eating foods that are rich in electrolytes, such as bananas or coconut water, can help replenish them.
- Increase fruit and vegetable intake: Fruits and vegetables contain a lot of water, which can help keep you hydrated. They also provide essential vitamins and nutrients that support overall health.
By following these tips, you can maintain a healthy diet and hydration levels to reduce the risk of blood in stool after drinking. Remember to seek medical attention if you have any concerning symptoms or if your condition worsens.
Seeking Medical Attention And Proper Treatment
Alcohol consumption can have serious health implications, including the presence of blood in your stool. Seeking medical attention and proper treatment is crucial for preventing and managing potential hematological complications associated with alcohol use disorder.
Getting timely medical care helps prevent possible life-threatening complications that may arise from untreated bloody stools. It’s essential to discuss any symptoms you’re experiencing, including unusual bowel movements, with your doctor so they can assess the condition appropriately and provide appropriate treatment options to manage this problem effectively.
Treatment And Home Remedies For Relief
Medical diagnosis and treatment is important for blood in stool after drinking. However, there are also home remedies that can help alleviate symptoms such as drinking plenty of water, consuming a high fiber diet, taking over-the-counter medications like antacids or anti-inflammatory drugs, and avoiding alcohol altogether.
Medical Diagnosis And Treatment
If you’re experiencing blood in your stool after drinking, it’s important to seek medical attention. Here are some of the diagnostic tests and treatment options that may be recommended:
- Endoscopy: This procedure involves inserting a flexible tube with a camera into the digestive tract to look for signs of damage or bleeding.
- Fecal occult blood test: This test checks for hidden blood in the stool that may not be visible to the naked eye.
- Proctitis treatment: If inflammation of the rectum is causing rectal bleeding, treatments such as antibiotics, suppositories or creams may be prescribed.
- Radiation proctitis treatment: Radiation therapy can cause inflammation and bleeding in the rectum, and treatments may include medication or surgery to repair damaged tissue.
It’s important to remember that treatment will depend on the underlying cause of your symptoms. In some cases, simple measures like adjusting your diet or reducing alcohol consumption may be sufficient. However, if more serious issues like gastrointestinal ulcers or colon cancer are involved, more invasive treatments such as surgery or chemotherapy may be necessary. Always consult with a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment options.
Home Remedies For Relief
If you are experiencing blood in stool after drinking, there are some home remedies that may help relieve your symptoms. Here are some of the most effective home remedies:
- High fiber foods: Eat foods that are high in fiber to help prevent constipation, which can cause rectal bleeding. Some examples of high fiber foods include green vegetables, beans, squash, prunes, and figs.
- Herbal remedies: Certain herbs such as chamomile tea have been associated with increased urinary levels of hippurate and glycine which can help with gastrointestinal issues.
- Warm bone broths: Drinking warm bone broths can also provide relief for constipation and rectal bleeding.
- Sitz bath: A sitz bath can be done at home to help soothe hemorrhoids and other anal irritations.
- Ice packs: Applying an ice pack to the affected area can help reduce inflammation and pain caused by hemorrhoids or other anal irritations.
By incorporating these home remedies into your daily routine while limiting alcohol consumption and maintaining a healthy diet and hydration levels, you may find relief from the symptoms of blood in stool after drinking. However, it is important to remember that seeking medical attention and proper treatment is always recommended if symptoms persist or worsen.
Conclusion
In conclusion, experiencing blood in stool after drinking is a serious sign of an underlying medical condition that should not be ignored.
Limiting alcohol consumption, maintaining a healthy diet and hydration, and seeking proper treatment are key steps for preventing or managing this condition.
Remember to consult with your healthcare provider if you experience any symptoms or changes in bowel movements after consuming alcohol.
Sources: https://chesbrewco.com
Category: Drink