Wondering how that smooth, clear spirit in your cocktail came to be?
Vodka, one of the world’s most popular alcoholic beverages, has a fascinating production process.
You Are Watching: How Is Vodka Made Updated 12/2025
In this article, we will delve into everything from the raw materials used in making vodka to its distillation and bottling stages.
Ready for a spirited journey through the art of vodka-making? Let’s get started!
The Basics of Vodka Production
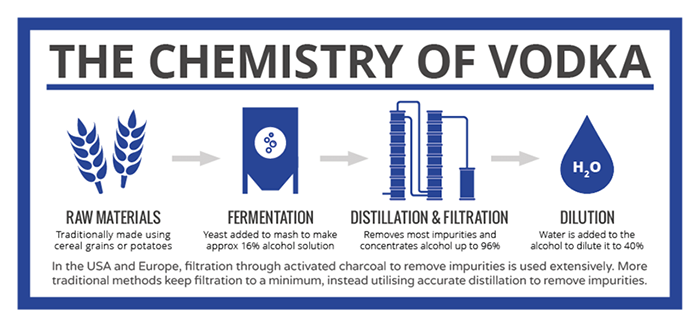
Vodka production begins with the fermentation process using ingredients like grains, potatoes, or fruit to create a base liquid with high alcohol content.
Ingredients used in vodka production
Vodka production involves a select group of ingredients that are subjected to careful processes. The primary ingredient is water, which constitutes almost 60% of the drink.
It’s crucial that this water be pure and mineral-rich, as its quality can significantly affect the taste of the vodka.
Fermentation process
Vodka is made through a process called fermentation. During this process, the raw materials used to make vodka undergo a chemical reaction that converts sugars into alcohol.
Here’s how the fermentation process works:
- Raw Materials: Vodka can be made from a variety of raw materials, including grains like rye, rice, wheat, and vegetables like corn and potatoes.
- Starch Conversion: If grains are used as the base ingredient, such as wheat or rye, they need to be converted into fermentable sugars before fermentation can occur. This is done by grinding the grains and mixing them with water to create a mash.
- Enzyme Addition: Enzymes are added to the mash to break down the starches into simpler sugars that yeast can ferment.
- Yeast Fermentation: Yeast is then added to the mash, which consumes the sugars and converts them into alcohol through a process known as alcoholic fermentation. The yeast produces ethanol and carbon dioxide as byproducts.
- Temperature Control: The fermentation process typically takes place at controlled temperatures between 75-95 degrees Fahrenheit (24-35 degrees Celsius) to ensure optimal yeast activity and alcohol production.
- Duration of Fermentation: The fermentation process usually takes several days to a couple of weeks depending on various factors such as temperature, type of raw material used, and desired alcohol content.
- Alcohol Content: At the end of the fermentation process, the resulting liquid is referred to as “wash” or “distiller’s beer” with an alcohol content of about 8-15% ABV (alcohol by volume).
- Taste Development: During fermentation, flavors may develop in the wash due to various factors such as yeast strain used and impurities in the raw materials.
Distillation process
To understand how vodka is made, it’s essential to know about the distillation process. Distillation is a crucial step in producing high-quality vodka.
Here’s an overview of the distillation process:
- Fermentation: Before distillation can take place, the raw materials used to make vodka go through a fermentation process. This involves converting sugars into alcohol with the help of yeast.
- Batch or Continuous Distillation: There are two main methods of distilling vodka – batch distillation and continuous distillation.
- Batch Distillation: In this traditional method, small batches of fermented liquid are distilled in pot stills. The liquid is heated, and as the temperature rises, alcohol vaporizes and rises through a column.
- Continuous Distillation: This method involves using large column stills that enable a continuous flow of liquid through the system. The liquid is heated at the bottom of the column, and as it rises, different compounds separate based on their boiling points.
- Multiple Distillations: Vodka typically undergoes multiple distillations to remove impurities and achieve a higher level of purity. Each distillation further purifies the alcohol by separating it from any unwanted substances.
- Filtration: After distillation, many vodka producers choose to filter their product to ensure maximum purity and smoothness. Common filtration methods include activated carbon filters or charcoal filters that help remove any remaining impurities.
- Dilution: Once the desired level of purity is achieved, water is added to dilute the distilled alcohol to its desired strength before bottling.
Filtration process
Vodka goes through a filtration process to remove any impurities and ensure a smooth, pure taste. Here’s how it works:
- Charcoal filtration: The vodka is passed through activated charcoal filters to remove unwanted flavors and odors.
- Multiple filtrations: Some vodka brands opt for multiple rounds of filtration to achieve the desired level of purity. This can involve passing the vodka through different types of charcoal or other filtering materials.
- Carbon filtration: Carbon filters are commonly used in the filtration process to further refine the vodka and remove any remaining impurities.
- Microfiltration: Some premium vodka brands employ microfiltration techniques, which use microscopic pores to filter out even the tiniest particles.
- Distillation as filtration: Vodka is distilled multiple times during production, which also acts as a form of filtration by separating alcohol from other components.
Different Methods of Vodka Production
There are various methods of vodka production, including grain-based vodka, potato-based vodka, and fruit-based vodka.
Discover the unique processes that give each type its distinct flavors and characteristics.
Grain-based vodka

Grain-based vodka is one of the most common types of vodka produced. It is made by fermenting and distilling grains like wheat, rye, barley, or corn.
Read More : Kirkland Vodka Grey Goose Updated 12/2025
The process begins with the selection of high-quality grains, which are then milled to expose their starches.
These starches are converted into sugars through a fermentation process using yeast. Once fermented, the mixture is distilled multiple times to remove impurities and create a high-proof alcohol base.
Finally, the alcohol is diluted with water to achieve the desired proof level before being bottled and packaged for consumption.
Grain-based vodkas have a smooth taste profile and are known for their versatility in cocktails and mixed drinks.
Potato-based vodka

Potato-based vodka is a popular alternative to grain-based vodka for those with gluten sensitivities. It is made by fermenting and distilling potatoes, resulting in a smooth and creamy flavor profile.
The use of potatoes as the main ingredient gives this type of vodka a unique character, often described as earthy or nutty.
Not only does potato-based vodka provide an excellent option for individuals looking for gluten-free alternatives, but it also adds diversity to the world of vodka production.
So if you’re seeking a different taste experience, give potato-based vodka a try!
Fruit-based vodka

Fruit-based vodka is a popular variation of this versatile spirit. Instead of using grains or potatoes, fruits like berries, apples, grapes, and citrus are used to create unique flavors.
The process involves fermenting the sugars in the fruit juice or puree and then distilling it to produce a smooth and fruity vodka.
Some brands infuse additional natural flavors into the vodka to enhance the taste even further.
This type of vodka offers a refreshing option for those seeking a fruity twist in their drinks while enjoying all the qualities that make vodka so beloved worldwide.
Flavoring Vodka
Infusion process
- Vodka can be infused with various flavors to create different taste profiles.
- The infusion process involves adding natural ingredients, such as fruits, herbs, or spices, to vodka and letting them steep for a certain period of time.
- During the infusion process, the flavors from the added ingredients are extracted into the vodka, creating a unique and flavorful drink.
- Infused vodka can have a wide range of flavors, including citrus, berry, herbal, spicy, or even chocolate.
- The length of time for infusion varies depending on the desired intensity of flavor. Some infusions may take days or weeks to fully develop their flavors.
- Infused vodkas can be enjoyed straight on the rocks or used as a base for cocktails and mixed drinks.
- Popular infused vodka flavors include lemon-infused vodka for refreshing summer cocktails and vanilla-infused vodka for creamy dessert-inspired drinks.
- Infusing vodka at home has become popular among cocktail enthusiasts who enjoy experimenting with different flavor combinations.
- Infused vodka can also be made commercially by distilleries who specialize in crafting unique flavored vodkas to cater to various taste preferences.
Additives and flavorings
When it comes to vodka production, additives and flavorings can play a significant role in enhancing the taste and aroma of the final product.
While traditional vodka is known for its clean and neutral flavor profile, some producers choose to add additional flavors to cater to specific preferences.
Here are some common additives and flavorings used in vodka production:
- Natural Ingredients: Many vodka producers use natural ingredients like fruits, herbs, spices, or botanicals to infuse flavors into their vodka. Examples include lemon, lime, raspberry, cherry, ginger, vanilla, or even jalapeno.
- Artificial Flavorings: Some vodka brands opt for artificial flavorings instead of natural ingredients. These synthetic compounds mimic the taste of various fruits or other flavors without using the actual ingredient.
- Sweeteners: Vodka manufacturers sometimes add sweeteners like sugar or honey to create a sweeter profile. This is often done in flavored vodkas that are meant to be enjoyed on their own or mixed into cocktails.
- Essences and Extracts: Vodka can also be flavored using essences and extracts derived from natural sources. These concentrated liquids contain the essential oils and flavors extracted from fruits or other aromatic substances.
- Aging: While aging is not as common with vodka as it is with spirits like whiskey or rum, some producers choose to age their vodka in wooden barrels to impart subtle flavors from the wood.
- Proofing Agents: To adjust the alcohol content of their products, distillers may use proofing agents such as water or ethyl alcohol derived from agricultural sources.
The Final Steps in Vodka Production
After the distillation process, vodka is then bottled and packaged, undergoing rigorous quality control measures to ensure consistency and purity.
Read More : What Is Armagnac Updated 12/2025
Additionally, there are legal regulations in place that dictate the production of vodka, ensuring that it meets certain standards before it can be sold.
With a multitude of popular vodka brands available on the market, consumers have plenty of options to choose from when it comes to their favorite spirit.
Bottling and packaging
Bottling and packaging are crucial steps in the vodka production process. After the vodka has been distilled and filtered, it is ready to be bottled and packaged for distribution.
Here’s a look at what happens during this stage:
- Bottling: The vodka is transferred from large storage tanks to individual bottles. The bottles used for vodka are typically made of glass, as it helps preserve the taste and quality of the spirit. The bottles are carefully filled with the clear liquid, ensuring precise measurements.
- Labeling: Once the bottles are filled, they are labeled with important information such as brand name, alcohol content, and country of origin. Labels may also include additional details such as tasting notes or awards won by the vodka.
- Packaging: After labeling, the bottles are placed in packaging materials such as cardboard boxes or gift sets. These packages not only protect the vodka during transportation but also serve as an attractive presentation for consumers.
- Quality control measures: Before leaving the distillery, each bottle goes through rigorous quality control checks to ensure that it meets industry standards. This includes checking for any defects in the bottle or packaging, verifying proper sealing to prevent leakage, and confirming accurate labeling.
- Legal regulations: Vodka production is subject to specific legal regulations in different countries. These regulations govern aspects such as labeling requirements, alcohol content limits, and geographic indications (e.g., “Russian Vodka”). Distilleries must comply with these regulations to ensure their products meet legal standards.
- Popular vodka brands: There are numerous well-known vodka brands available worldwide that have their own unique bottling and packaging designs. Some brands opt for sleek and minimalist designs while others embrace colorful graphics or distinctive shapes for their bottles.
Quality control measures
Quality control measures play a crucial role in ensuring the production of high-quality vodka. Here are some important aspects that manufacturers focus on:
- Raw material selection: Vodka producers carefully select and source the highest quality grains or potatoes to ensure the best base for their product.
- Rigorous testing: Throughout the production process, samples are regularly taken to test for impurities, consistency, and alcohol content. This helps maintain the desired taste and quality.
- Distillation process: Vodka is typically distilled multiple times to remove any impurities and create a smooth, clean flavor profile.
- Filtration: Filtration is an essential step in vodka production to further remove impurities and refine the spirit. This ensures a clear, pure final product.
- Tasting panels: Quality control teams conduct regular taste tests to evaluate the flavor and character of the vodka. This helps identify any inconsistencies or deviations from established standards.
- Packaging inspection: Vodka bottles undergo careful inspection for defects or damage before they are filled and sealed. This ensures that consumers receive products in perfect condition.
- Compliance with regulations: Vodka manufacturers adhere to strict legal regulations governing alcohol production, including labeling requirements, alcohol content limits, and purity standards.
Legal regulations for vodka production
Vodka production is subject to strict legal regulations in order to ensure safety, quality, and consistency.
These regulations vary from country to country but generally include guidelines on ingredients, processing methods, labeling requirements, and alcohol content.
For example, in the United States, vodka must be distilled at or above 190 proof (95% alcohol by volume) and can only contain water and ethanol as ingredients.
Any additions or flavorings must be clearly mentioned on the label.
Additionally, producers are required to meet certain standards of hygiene and cleanliness during the manufacturing process.
These regulations are put in place to protect consumers and maintain the integrity of vodka as a high-quality spirit.
Popular vodka brands
Vodka is enjoyed worldwide, and various brands have garnered recognition for their integrity, flavor, and quality.
Let’s delve into some of these popular vodka brands which have solidified their reputation in the vodka market.
| Brand | Origin | Known For |
|---|---|---|
| Absolut | Sweden | High-quality grain vodka with various creative flavors. |
| Smirnoff | Russia | One of the world’s most sold vodka brands, known for its affordability and range of flavors. |
| Grey Goose | France | Regarded as a top-shelf vodka. Known for its smoothness and wheat-based production. |
| Belvedere | Poland | Premium brand using Polish rye in its production, offering a unique and full-bodied flavor. |
| Stolichnaya | Russia | Balanced, quality vodka, made from wheat and rye grains. Offers a range of flavored vodkas. |
| Ketel One | Netherlands | A wheat-based vodka, known for its distinctive, crisp taste and smooth finish. |
| Ciroc | France | Unique for being made from grapes instead of grains. Offers a rich, fruity taste. |
| Tito’s | United States | American brand, corn-based, known for its smooth, clean taste. |
| Skyy | United States | Affordable brand, made from grains, known for its quadruple distillation process for purity. |
| Svedka | Sweden | Competitively priced, made from winter wheat, offers a variety of flavored vodkas. |
Understanding the origin and unique features of these popular brands can enhance your appreciation for this versatile spirit.
Conclusion
In conclusion, vodka is made through a meticulous process involving fermentation, distillation, and filtration. It can be produced from various raw materials such as grains like rye and wheat or vegetables like potatoes.
Vodka is known for its purity and versatility, making it one of the most popular alcoholic beverages worldwide.
Whether you prefer grain-based or potato-based vodka, the craftsmanship behind its production ensures a smooth and enjoyable drinking experience.
Cheers to the fascinating world of vodka-making!
Sources: https://chesbrewco.com
Category: Wine










