Do you chug down Gatorade and find yourself running to the restroom more often? Well, it’s not a mere coincidence. This blog will dive into the complex relationship between Gatorade – a favored drink among athletes for hydration, packed with electrolytes yet high in sugar, and the frequency of your bathroom visits.
Stick around to unravel this intriguing query – Does Gatorade make you pee?.
You Are Watching: Does Gatorade Make You Pee Definitive Guide Updated 07/2025
Understanding Electrolytes and Urination

Electrolytes are essential minerals that help maintain the balance of fluids in our bodies and play a role in various bodily functions, including urine production.
What are electrolytes?
Electrolytes are small, charged particles found in your body that carry out crucial functions to keep you healthy. These include minerals like sodium, potassium, and chloride. They help maintain hydration in the body, balance blood acidity and pressure, and enable muscles to contract properly.
Electrolytes often get lost in sweat during intense physical activities or when a person is dehydrated due to alcohol consumption. That’s why drinks such as Gatorade contain electrolytes – they aim to replenish these important particles in your body after they’ve been depleted.
But it’s also crucial to note that too much of certain electrolytes can have negative effects on health; for example, an excess intake of sodium might increase blood pressure.
How do electrolytes affect urine production?
Electrolytes play a significant role in urine production. Specifically, sodium and potassium, which are common electrolytes found in drinks like Gatorade, can impact the amount of urine produced by the body.
When these electrolytes are present in high concentrations, they help to retain water in the body and reduce urination. This is because water follows the salt through a process called osmosis.
So, when you consume beverages with electrolytes like Gatorade, it can affect your urinary system by influencing how much urine your body produces.
The Impact of Gatorade on Urination
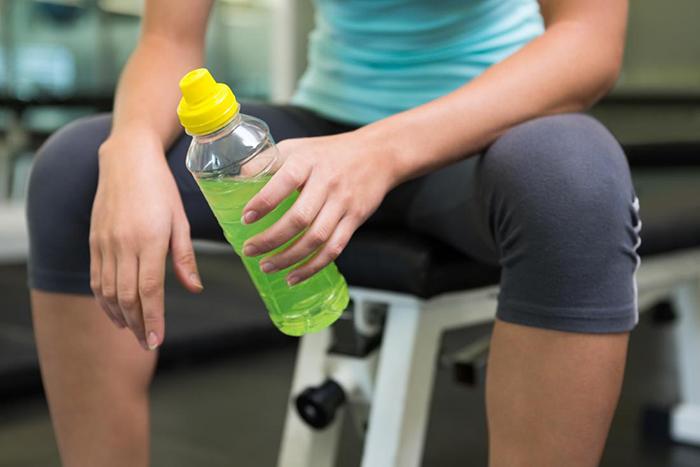

Gatorade’s electrolyte content can increase urine production due to its high concentration of sodium and potassium.
The electrolyte content of Gatorade
Gatorade is known for its electrolyte content, which includes sodium and potassium. These minerals help replenish the body’s fluids and electrolytes when dehydrated. However, it’s important to note that Gatorade also has a high concentration of sugar.
A 12-oz bottle contains 21 grams of added sugar, which can be a concern for some individuals, especially those who need to watch their sugar intake. It’s essential to be mindful of the electrolyte benefits but also consider alternative options for hydration, especially if you are looking to reduce your sugar consumption.
How Gatorade can increase urine production
Gatorade, a popular sports drink, has the potential to increase urine production due to its electrolyte content. Studies have found that Gatorade can raise urinary sodium and chloride levels compared to water and baseline levels.
The high concentration of sodium in Gatorade actually helps minimize urination by following the principle of osmosis – water flows towards areas with higher salt concentrations. However, it is important to be aware that Gatorade also contains a significant amount of added sugar, which should be considered when consuming this drink.
Overall, while Gatorade can increase urine production, it still serves as an option for hydration during physical activity due to its electrolytes content.
Potential risks and side effects
Gatorade, while popular for its rehydrating capabilities, does come with potential risks and side effects. It is important to be aware of these before consuming the drink. Here are some potential risks and side effects associated with Gatorade:
- High sugar content: Gatorade contains a high concentration of added sugar, with a 12-oz bottle containing 21 grams. Consuming excessive amounts of sugar can lead to weight gain, tooth decay, and an increased risk of developing chronic diseases like diabetes.
- Electrolyte imbalances: Although Gatorade is designed to replenish electrolytes lost during physical activity, consuming it excessively or without the need for rehydration can disrupt the balance of electrolytes in the body. This can lead to issues such as muscle cramps, weakness, and irregular heart rhythms.
- Dehydration: While Gatorade is intended to hydrate, consuming it in large quantities without adequate water intake can have the opposite effect. The high concentration of electrolytes in Gatorade may contribute to dehydration if not balanced with enough water consumption.
- Potential allergic reactions: In some cases, individuals may have allergies or sensitivities to certain ingredients in Gatorade, such as artificial dyes or flavors. Allergic reactions can range from mild symptoms like hives and itching to more severe reactions like difficulty breathing or anaphylaxis.
- Blood pressure concerns: Due to its sodium content, regularly consuming Gatorade may potentially increase blood pressure levels, especially in individuals who are sensitive to sodium.
- Dental health issues: The high sugar content in Gatorade combined with its acidity can contribute to tooth enamel erosion and dental cavities if consumed frequently without proper oral hygiene practices.
Comparing Gatorade to Other Electrolyte-Based Drinks

Gatorade and Pedialyte have different electrolyte compositions, with Gatorade containing higher concentrations of sodium and potassium.
Differences between Gatorade and Pedialyte
Read More : Can You Bring A Drink Into A Restaurant Updated 07/2025
Gatorade and Pedialyte, both popular hydration drinks, have significant differences in their compositions and intended uses. While Gatorade is marketed as an exercise enhancement drink, Pedialyte is often used for rehydration during illness.
Here is a comparison of the two in terms of their composition, intended use, and potential side effects:
| Gatorade | Pedialyte | |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | High in electrolytes but also contains 21 grams of sugar per 12-ounce serving. | Lower sugar content and more electrolytes, including sodium and potassium. |
| Intended Use | Marketed as an exercise enhancement drink, suitable for hydration during physical activity. | Used for rehydration, especially during illness and dehydration, making it a potential choice for those dealing with alcoholism. |
| Potential Side Effects | Due to high sugar content, it can lead to weight gain and tooth decay if consumed in excess. | Minimal side effects with more balanced electrolyte content, making it a safer option for long-term use. |
Benefits and risks of electrolyte-based drinks
Electrolyte-based drinks like Gatorade and Pedialyte offer several benefits but also come with risks. Consider the following:
- Replenish water and minerals: Electrolyte-based drinks can help replenish the body’s water and minerals, including sodium and electrolytes, especially when dehydrated.
- Hydration during physical activity: Sports drinks like Gatorade are designed to provide hydration during intense exercise or prolonged physical activity, helping to replace fluids lost through sweat.
- Restoring electrolyte balance: Electrolytes play a crucial role in maintaining proper fluid balance in the body. Drinking electrolyte-based beverages can help restore these levels and prevent imbalances.
- Improved performance: By replenishing electrolytes, these drinks can enhance athletic performance by improving hydration and reducing muscle cramps caused by dehydration.
- Convenient source of nutrients: For individuals who struggle to meet their daily fluid intake or have specific dietary restrictions, electrolyte-based drinks can provide a convenient and accessible source of necessary nutrients.
- High sugar content: One significant risk associated with many electrolyte-based drinks is their high concentration of added sugars. Excessive sugar intake can contribute to weight gain, tooth decay, and other health issues if consumed regularly.
- Diuretic effects: Some sports drinks may have diuretic effects due to certain ingredients or high sugar content, leading to increased urination rather than optimal hydration.
- Not always necessary: While beneficial for athletes or those engaging in intense physical activity, electrolyte-based drinks are not always necessary for everyday hydration needs. In most cases, water is sufficient for staying hydrated throughout the day.
When to choose Gatorade or alternative options
Gatorade is a popular choice for athletes and individuals who engage in rigorous physical activity. It helps replenish electrolytes like sodium and potassium that are lost through sweat, aiding in hydration.
If you’re an athlete or someone who exercises regularly, Gatorade can be a suitable option to keep your body hydrated during intense workouts.
However, it’s important to note that Gatorade contains a high concentration of sugar. Therefore, if you’re looking for alternative options with fewer calories or if you have concerns about your sugar intake, there are other electrolyte-based drinks available.
For instance, Pedialyte is another effective option that helps restore water and minerals when dehydrated without the added sugars found in Gatorade.
Ultimately, your choice between Gatorade and alternative options will depend on your specific needs and preferences. It’s essential to consider factors like the duration and intensity of your physical activity as well as any dietary restrictions or health conditions you may have.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Gatorade can increase urination due to its electrolyte content and high concentration of sugar. While it can be beneficial for athletes during intense exercise, it’s important to consider the sugar intake and explore alternative hydration options.
Understanding the impact of Gatorade on urination helps make informed choices for optimal hydration.
Sources: https://chesbrewco.com
Category: Drink