Have you ever wondered, “is water heavier than sand?” Surprisingly, when measuring the same volume of each substance, sand comes out on top. This article is about to dive into the intricacies of density and weight comparisons between beach favorites: water and sand.
Stay curious; an exciting discovery awaits!
You Are Watching: Is Water Heavier Than Sand Updated 07/2025
Density Comparison: Water Vs Sand

Sand is denser than water, with dry sand weighing between 80-100 pounds per cubic foot, while water has a density of 62.4 pounds per cubic foot.
Sand Is Denser Than Water
Regular, dry sand packs quite a punch in the weight department due to its density. With each cubic foot weighing between 80 and 100 pounds, it’s significantly denser than water which only hits the scales at 62.4 pounds per cubic foot.
This means if you had two containers of equal volume, one filled with water and the other with sand, your muscles would be working much harder when lifting that sandy vessel! It’s this superior density that not only gives sand more heft but also makes it an important tool in multiple applications such as construction projects or even weighing down umbrella bases.
So, next time you feel fatigued after building a monumental castle on the beach or moving bags of gardening sand around your yard, remember – those tiny grains are heavier than they appear!
Dry Sand Weighs Between 80-100 Pounds Per Cubic Foot
Dry sand is a relatively heavy substance, with a weight range of 80-100 pounds per cubic foot. This means that if you were to take a cubic foot of dry sand and measure its weight, it would fall within this range.
The density of sand is what gives it this weight, as it is denser than water. This characteristic makes sand an ideal material for various applications in construction and landscaping, where stability and weight are important factors.
Whether used in umbrella bases or concrete mixtures, the weight of dry sand plays a crucial role in its functionality and effectiveness.
Water Has A Density Of 62.4 Pounds Per Cubic Foot
Water, the essential substance for life, has a density of 62.4 pounds per cubic foot. In simpler terms, this means that if you were to take a cubic foot of water and weigh it, it would be about 62.4 pounds.
Read More : How Much Sugar In A Twisted Tea Updated 07/2025
Comparing this to sand, which is denser than water, highlights the differences in weight between the two substances. While water may seem lighter and more fluid than sand, its density reveals that it still carries significant mass and weight within its volume.
Weight Comparison: Water Vs Sand
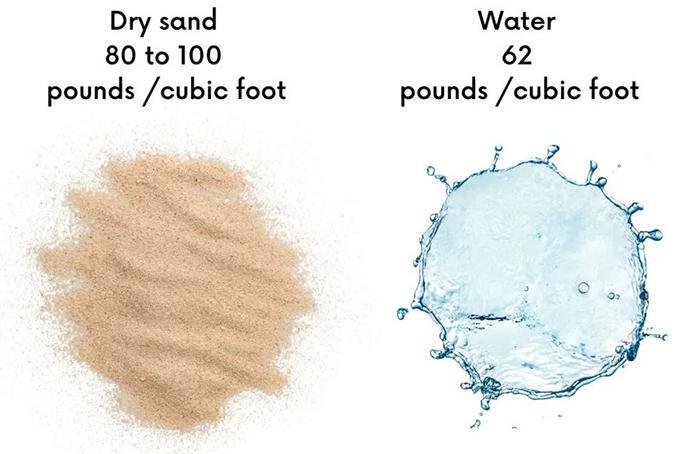

Sand Weighs More Than Water When Compared By Volume
Sand is heavier than water when you compare them in terms of volume. This is because sand has a higher density than water, meaning it has more mass packed into the same amount of space. Dry sand typically weighs between 80 and 100 pounds per cubic foot, while water has a density of about 62.4 pounds per cubic foot.
So, if you were to fill two containers with the same volume of sand and water, the container filled with sand would be heavier. Additionally, wet sand weighs even more due to the added weight of the water within it.
That’s why sand is often used as a reference point for determining the weight or density of other substances. Its heaviness makes it ideal for applications like construction and landscaping where stability is important.
The Weight Of Sand Depends On Its Moisture Content
The weight of sand can be influenced by its moisture content. When sand is dry, it weighs between 80 and 100 pounds per cubic foot. However, when water is present in the sand, such as after rainfall or near bodies of water, the moisture adds additional mass to the overall weight.
Wet sand will weigh more than dry sand due to the added weight of the water within it. This difference in moisture content affects not only the weight but also how compacted or loose the sand may be.
Overall, understanding and considering the moisture content of sand is important when determining its application or comparing it to other substances.
Factors Affecting Weight Comparison

The weight of sand can be influenced by factors such as its moisture content, particle size and composition, and the level of compaction.
Moisture Content Of The Sand
The moisture content of sand plays a significant role in its weight. When sand is wet, it becomes heavier due to the added mass of the water present within it. This is why we often notice that wet sand feels denser and harder to move compared to dry sand.
The amount of water absorbed by the sand can vary depending on factors such as humidity and exposure to moisture sources like rain or underground springs. It’s important to consider the moisture content when evaluating the weight of sand, especially in construction and landscaping applications where stability and load-bearing capacity are crucial factors.
Particle Size And Composition Of The Sand
Read More : Best Most Expensive Starbucks Birthday Drink Updated 07/2025
The weight of sand can vary depending on its particle size and composition. Finer sands, like those used for construction purposes, tend to have a higher density and therefore weigh more than coarser sands.
This is because smaller particles pack more closely together, increasing the overall mass per volume. Additionally, the composition of the sand can also affect its weight. For example, sand that contains heavier minerals or rocks will be denser and therefore heavier than sand composed mainly of lighter materials.
Understanding these factors is important when considering the weight of sand in various applications, such as determining the stability of structures or selecting appropriate materials for landscaping projects.
Compaction Of The Sand
Sand compaction refers to the process of compressing sand particles together, reducing the volume and increasing its density. When sand is compacted, it becomes more stable and able to bear weight without shifting or settling.
This is important for various applications in construction and landscaping where stability is essential.
During the compaction process, pressure is applied to the sand, causing the particles to come closer together. The result is a reduction in air voids between individual grains, leading to increased density.
Compacted sand has a higher mass per unit volume compared to loose or uncompacted sand.
Compaction can be achieved through different methods such as mechanical compaction with vibrating plates or rollers, as well as natural processes like moisture saturation that help bind the particles together.
The level of compaction required depends on factors such as intended use, soil conditions, and load-bearing capacity needed for specific projects.
Properly compacted sand not only provides stability but also enhances drainage properties by creating pathways for water flow through interconnected spaces within the material. This makes it particularly useful in preventing waterlogging issues commonly associated with poorly drained areas.
Conclusion
In conclusion, when comparing the weight of water and sand, it is important to consider their densities. While sand is denser than water and therefore weighs more per unit volume, the actual weight can vary depending on moisture content and other factors.
Overall, sand is heavier than water, making it a practical choice for various applications in construction and landscaping.
Sources: https://chesbrewco.com
Category: Drink