Navigating the world of sports drinks while on a low FODMAP diet can be tricky. Take Gatorade, for example – it’s not typically considered low FODMAP due to ingredients like high fructose corn syrup and maltodextrin.
In this blog post, we’re going to break down what makes a beverage low FODMAP, examine the contents of Gatorade, and provide you with some healthy alternatives. Let’s dive in; your gut health will thank you!
You Are Watching: Gatorade Low Fodmap Updated 07/2025
Is Gatorade Low FODMAP Friendly?

Gatorade is not considered low FODMAP friendly due to the presence of high fructose corn syrup, maltodextrin, and monosodium glutamate.
Ingredients to be cautious of (high fructose corn syrup, maltodextrin, monosodium glutamate)
In the quest for a low FODMAP-friendly sports drink, certain ingredients merit caution due to their potential effects on digestive health. Here’s a rundown of some key offenders found in Gatorade:
- High Fructose Corn Syrup: This sweetener is notorious for its high fructose content and it’s often used in popular sports drinks like Gatorade. The issue with fructose is that it can cause digestive discomfort in people with IBS or other gastrointestinal problems.
- Maltodextrin: Another ingredient commonly found in Gatorade, maltodextrin could pose problems for those following a low FODMAP diet because it can increase gas, bloating and stomach cramps in some individuals.
- Monosodium Glutamate (MSG): Often used to enhance flavor, MSG has been linked to adverse reactions such as headache, flushing, sweating, and digestive issues —not ideal issues for someone aiming to keep IBS symptoms at bay.
Fructose content and its impact on FODMAP sensitivity
Gatorade and other sports drinks often contain fructose, a type of sugar that can be problematic for individuals with FODMAP sensitivity. FODMAPs are carbohydrates that can cause digestive symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, and diarrhea in some people.
Fructose is one of the FODMAPs to watch out for because it can be difficult to digest for those with sensitive stomachs. When consuming high amounts of fructose, especially when combined with other FODMAPs like sorbitol or polyols found in certain fruits and sweeteners, it can trigger uncomfortable gut reactions.
Read More : Why Did They Discontinue Pear Red Bull Updated 07/2025
This is why individuals following a low FODMAP diet should take caution when drinking Gatorade or similar sports drinks containing fructose.
Gatorade Alternatives for a Low FODMAP Diet
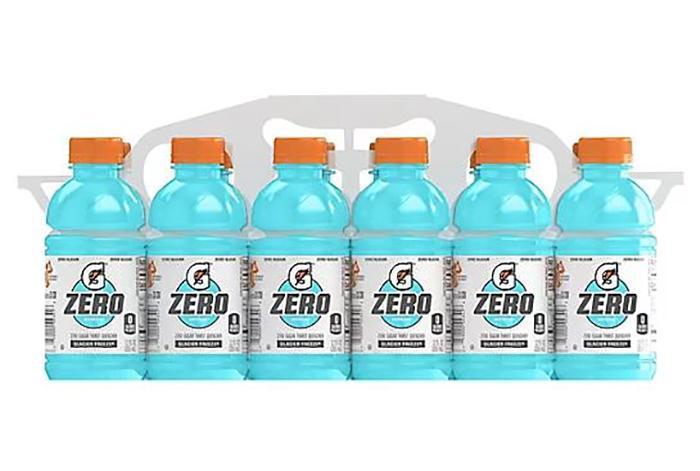

When following a low FODMAP diet, it’s important to find Gatorade alternatives that won’t trigger symptoms, such as low FODMAP sports drinks and homemade electrolyte drink recipes.
Low FODMAP sports drinks options
If you’re following a low FODMAP diet and looking for suitable sports drinks, here are some options to consider:
- Gatorade Thirst Quencher Fierce Orange Sports Drink: This flavor of Gatorade is compatible with various diets, including vegan, vegetarian, pescatarian, gluten-free, and low FODMAP.
- Powerade: Similar to Gatorade, Powerade is another sports drink that may be low FODMAP. It’s worth checking the ingredients to ensure it aligns with your dietary needs.
- Pedialyte: While primarily marketed as a rehydration solution for children, many adults find Pedialyte effective for replenishing electrolytes. Some varieties may be low FODMAP-friendly.
- Nuun: This popular brand offers electrolyte tablets that can be dissolved in water to create a hydrating beverage. Check the ingredients to confirm if they fit within your low FODMAP requirements.
- Homemade recipes: If you prefer more control over the ingredients in your sports drinks, consider making your own at home. There are plenty of recipes available online for creating low FODMAP electrolyte drinks using natural ingredients.
Homemade electrolyte drink recipes
- Stay hydrated and support your alcohol recovery with these homemade electrolyte drink recipes.
- Mix 1 cup of coconut water, 1 cup of water, and a pinch of sea salt for a refreshing and replenishing beverage.
- Combine 1 cup of unsweetened almond milk, 1 tablespoon of maple syrup, and a dash of sea salt for a dairy-free electrolyte drink.
- Create a low FODMAP sports drink by blending together 1 cup of fresh orange juice, 2 cups of water, and a sprinkle of sea salt.
- For an extra boost, add a scoop of low FODMAP protein powder to any of these recipes to aid in muscle recovery.
- Experiment with different flavors by infusing your electrolyte drinks with sliced cucumber, mint leaves, or lemon wedges.
- Make a batch of homemade popsicles using your preferred electrolyte drink recipe for a cool and hydrating treat.
- Opt for natural sweeteners like maple syrup or stevia instead of high fructose corn syrup when making these drinks at home.
- Remember to sip on these homemade electrolyte drinks throughout the day to replenish important minerals lost during alcohol detoxification.
Considerations for Low FODMAP Fueling

When fueling on a low FODMAP diet, it’s essential to consider carbohydrate periodization and the train-low approach for optimal sports performance.
Carbohydrate periodization and train low approach
Carbohydrate periodization and the train low approach are strategies that can be incorporated into an athlete’s diet to optimize performance while following a low FODMAP regimen.
Read More : How To Know When Sodastream Is Empty Updated 07/2025
Carbohydrate periodization involves adjusting carbohydrate intake based on training demands, with higher intakes during intense training periods and lower intakes during lighter training or rest days.
This allows for better utilization of carbohydrates and improved overall performance. On the other hand, the train low approach involves completing some workouts in a fasted state or with reduced carbohydrate availability.
This helps improve metabolic efficiency, enhances fat burning capacity, and supports endurance adaptations. By combining these approaches with low FODMAP fueling options such as low FODMAP sports drinks or homemade electrolyte drinks, athletes can effectively manage their IBS symptoms while still maintaining peak performance levels.
Finding low FODMAP fueling options for sports performance
When it comes to sports performance, finding low FODMAP fueling options can be essential for individuals with alcoholism. Here are some options to consider:
- Look for sports drinks that are specifically labeled as low FODMAP or suitable for individuals with IBS.
- Opt for beverages that contain simple sugars like glucose or dextrose instead of fructose. Fructose can be a trigger for digestive symptoms in those with FODMAP sensitivity.
- Consider making your own homemade electrolyte drinks using ingredients that are low in FODMAPs, such as coconut water, lemon juice, and a pinch of salt.
- Experiment with different carbohydrate sources that are low in FODMAPs, such as rice cakes, gluten-free pretzels, or potato-based snacks.
- Incorporate easily digestible protein sources into your fueling routine, such as lean meats, eggs, or lactose-free dairy products.
- Hydrate adequately before, during, and after exercise to support optimal performance and recovery.
- Keep track of your symptoms and reactions to different fueling options to identify any potential triggers.
- Consult with a registered dietitian who specializes in sports nutrition and the low FODMAP diet for personalized guidance.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Gatorade is not considered low FODMAP friendly due to its ingredients such as high fructose corn syrup, maltodextrin, and monosodium glutamate.
Individuals with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or a sensitivity to FODMAPs should be cautious when consuming Gatorade or other sports drinks that contain fructose or maltodextrin.
However, there are alternative low FODMAP sports drinks available, as well as homemade electrolyte drink recipes that can meet the hydration needs of those following a low FODMAP diet. It’s important to prioritize digestive health and choose hydrating options that work best for one’s individual dietary needs.
Sources: https://chesbrewco.com
Category: Drink